P53 GENE THERAPY USING Helper Dependent Adenovirus: A REVIEW
Makhyan Jibril Al Farabi*
*)Master Degree Biomedical Study, Faculty of Medicine Brawijaya University
Cancer cells are abnormal cells which has uncontrollable proliferation. Cancer cell will able to migrate into other tissues in the body to develop new cancer lesion (Sofyan, 2000). Based on Household National Survey (2001), cancer has become the 5th cause of death in Indonesia, exactly after cardiovascular disease, infectious disease and gastrointestinal disorder with prevalence 3,4% in 1980 and 6% in 2001. Basic Health Research (2007) prove that the prevalence of cancer reach 4.3 of 1000 inhabitans (Ministry of Health, 2007). Indonesian Cancer Foundation state that in every year, 800.000 people in Indonesia will suffer from cancer (Kartika, 2007)
P53 as the one of tumor supressor gene in cancer, hold important role for protecting cell cycle process. If cells are damaged, p53 will induce cell into arrest state between G1 and S with inhibition of Cyclin D Kinase and DNA repair before cell entering S phase. Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by p53 depends on the cell enviroment and cell type. Inactivation of p53 mostly caused by mutation of an alele or deletion, the other one caused by lost of normal alele and deletion of chromosome segmen (Finlay et al., 1983).
Gene therapy is one of the promising disease treatment in the future, using gene insersion to treat abnormal cell will replace the damaged gene that cause disease into better one (Jusuf, 2009). Recent development of gene therapy suggest helper dependent adenovirus as the new plasmid with deleted most of adenoviral coding gene. helper dependent adenovirus has promising prospect for gene therapy as its toxicity is very low and safe (Sandig et al., 2000).
Mechanism of P53 Gene Therapy using Helper Dependent Adenovirus in Suppression of Cancer Cell Proliferation
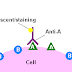
P53 repair with helper dependent adenovirus plasmid will begin after interaction between helper dependent adenovirus vector with cancer cell. Therefore, it will be a bound between knob domain from protein fiber with receptor in the cell (CD46 and CAR). This interaction continued to another interaction in which motif at penton protein base interact with αv integrin and stimulate cell signaling and actin polymerization to facilitate endocytotic process of viral particle with p53 gene via clathrin-coated pits (Morrisey et al., 2001).
After vector successfully enters the cell, endosome will undergo acidification that cause disassociation of the capsid and p53 will enter cytoplasm. This reaction followed by activation of microtubule that help p53 gene to enter into nucleus via nuclear pore to associate with histon molecules. P53 gene will substitute the mutated or deleted LOH so that the p53 function in the treated cell will become normal. Cancer cell with p53 gene repair will able to activate p21 whenever DNA of the cell is damaged. P21 will inhibit cyclin and CDK so that Rb will not undergo hyperphosporylization and E2F cannot transcript the gene. Therefore, cell will enter arrest state between G1 and S phase. This will lead into suppression of cancer cell proliferation.
Mechanism of P53 Gene Therapy using Helper Dependent Adenovirus in Induction of Cancer Cell Apoptosis
Research done by Agarwal et al.,(1998) show that p53 was able to either stop cell cycle or induce apoptosis in damaged cell. Administration of Ad5CMVp53 (Adenovirus mediated p53 treatment) previously was able to inhibit colorectal cancer development via apoptosis (Baek et al,. 2004). When mutated or deleted p53 in the cell has repaired, DNA damage in the cell will induce activation of p53 which will lead into BAX transcription in the mitochondria. BAX activation will induce release of c cytochrome that will form complex with APAF-1 (apoptosis-inducing factor 1), procaspase 9 and ATP. This complex will activate procaspase 9, thus activated caspase 9 will trigger caspase 3 activation. Finally, caspase 3 will execute the damaged cell via destruction of DNA and cancer cell component, this will lead into cancer cell apoptosis. (Cotran et al., 2007).
Another proposed apoptosis pathway with p53 gene therapy was previously described with Eichhorst and Krammer (2001) that show CD95 was regulated by p53 therefore damage in p53 will lead into CD95 impairment. Gene therapy with p53 will repair abnormal p53 thus activation of p53 will lead into increase of CD95 expression in the cancer cell. Therefore, CD95L/ Fas ligand will bind more into CD95 receptor, CD95 will undergo trimerization and its death domain cytoplasmic will attract FADD protein. FADD will recruit and activate procaspase-8 into caspase-8. Finally caspase-8 will activate caspase-3 that able to execute the damaged cell via destruction of DNA and cancer cell components, this will lead into cancer cell apoptosis. (Cotran et al., 2007). It can concluded that apoptosis-mediated effect of p53 gene therapy using helper dependent adenovirus will able to regress cancer development via induction of cytochrome c release by mitochondria or death-induced signaling complex with CD95.
REFERENCES
Agarwal ML, Taylor WR, Chernov MV, Chernova OB, Stark GR. 1998. The p53 network. J Biol Chem; 273: 1-4.
Baek, Jeong-Heum ,Munna L Agarwal, Raymond R Tubbs, Alex Vladisavljevic,Hiroshi Tomita, Ronald M Bukowski,Jeffrey W. Milsom, Jin-Man Kim, Jin-Young Kwak. 2004. In vivo Recombinant Adenovirus mediated p53 Gene Therapy in aSyngeneic Rat Model for Colorectal Cancer. J Korean Med Sci; 19: 834-41
Cotran, Ramzi S dan Stanley L. Robbins . 2007. Basic Pathology. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.
Ministry of Health in Indonesia (Depkes RI). 2007. Aktivitas Fisik dan Diet Seimbang Mencegah Kanker. http://www.promosikesehatan.com /?act=news&id=473/.htm. Acessed 13 March 2012 09.00 A.M
Eichhorst dan Krammer PH. , 2001. Derangement of apoptosis in cancer. Lancet 358:345
Finlay, Hinds, p.w. and Levine. 1983. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation, Cell, 57:1083-1093.
Jusuf, Ahmad Aulia. 2009. Terapi Gen Pada Manusia. Bagian Histologi:Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia
Kartika. 2007. 800.000 Orang Indonesia Terserang Kanker Tiap Tahun. http://www.suarapembaruan.com/News/2007/05/14/Utama/ut01.htm. Acessed 13 March 2012 09.05 A.M
Morrissey , Richard E., Christopher Horvath, Eileen A. Snyder, James Patrick dan James S., MacDonald. 2001. Rodent Nonclinical Safety Evaluation Studies of SCH 58500, an Adenoviral Vector for the p53 Gene. Toxicological Sciences 65, 266-275
Sandig, Volker, Rima Youil, Andrew J. Bett, Laura L. Franlin, Masanobu Oshima, Domenico Maione, Fubao Wang, Michael L. Metzker, Rocco Savino dan C. Thomas Caskey. 2000. Optimization of the helper-dependent adenovirus system for production and potency invivo .PNAS vol. 97 no. 3 1002-1007
Sofyan, Rochestry. 2000. Terapi Kanker pada Tingkat Molekuler.Cermin Dunia Kedokteran No. 127
Household National Survey. 2001. Gizi dan Promosi Kesehatan. http://www.promosikesehatan.com/?act=article&id=122. Acessed 13 March 2012 09.23 A.M
TERAPI GEN P53 BERBASIS PLASMID Helper
Dependent Adenovirus
Makhyan Jibril Al Farabi*
*)Pendidikan Master Degree Biomedik, Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas
Brawijaya
Sel kanker tumbuh secara tidak teratur, melanggar semua kaidah
normal, tidak peduli akan kontrol dalam perbanyakan, dan menggunakan agendanya
sendiri. Sifat lainnya adalah mempunyai kemampuan untuk bermigrasi dari
tempatnya tumbuh ke jaringan di dekatnya dan membentuk massa pada daerah baru
di dalam tubuh (Sofyan, 2000). Berdasarkan Survey Kesehatan Rumah Tangga (SKRT)
tahun 2001 penyakit kanker merupakan penyebab kematian nomor 5 di Indonesia
setelah penyakit kardiovaskuler, infeksi pernafasan dan pencernaan. Dengan peningkatan kasus kematian penyakit
kanker dari 3,4 % pada tahun 1980 menjadi 6 % pada tahun 2001. Berdasarkan Riset Kesehatan Dasar (Riskesdas)
tahun 2007, prevalensi tumor di Indonesia adalah 4,3 per 1000 penduduk, dan
kanker merupakan penyebab kematian nomor 7 (5,7%) (Depkes RI, 2007). Dari data
Yayasan Kanker Indonesia, disebutkan bahwa.tiap tahunnya 800.000 Orang
Indonesia Terserang Kanker (Kartika, 2007).
Salah satu gen penekan kanker adalah gen p53 yang merupakan pelindung
siklus sel. Bila sel terluka, p53 dalam inti memicu sel untuk melakukan
“arrest” pada perbatasan G1/S dengan menginduksi penghambat CDK (cyclin D
kinase) dan sistem perbaikan DNA terlebih dahulu menghilangkan luka tersebut
sebelum sel memasuki fase S tanpa adanya DNA yang terluka. Program “arrest” dan
apoptosis ini tergantung pada lingkungan fisiologik ataupun jenis sel. Oleh
karena itu kehilangan fungsi gen p53 ini merupakan penyebab munculnya
malignansi. Inaktivasi gen p53 ini biasanya terjadi dalam dua tahap yakni
inaktivasi pada satu alel oleh mutasi titik atau delesi kecil dan berikutnya
adalah kehilangan alel normal oleh delesi segmen kromosom (Finlay et al., 1983).
Terapi gen merupakan salah satu konsep yang menjanjikan untuk mengobati
penyakit tententu dengan cara menginsersikan gen yang telah diperbaiki atau gen
tertentu kedalam genom sel-sel atau
jaringan individu untuk menggantikan gen yang abnormal yang menyebabkan
terjadinya penyakit tersebut (Jusuf, 2009). Inovasi
mutkhir dalam modifikasi adenovirus yaitu helper
dependent adenovirus dimana hampir semua viral coding adenovirus telah
dihapus. helper dependent adenovirus menunjukkan
kemapuan yang menjanjikan dalam terapi gen, dimana toksisitasnya sangat minim
bahkan bisa dikatakan tidak ada sama sekali (Sandig et al., 2000).
Mekanisme Viroterapi Gen P53 Berbasis Helper Dependent Adenovirus dalam Menghambat Proliferasi Sel
Kanker
Perbaikan gen P53 oleh plasmid helper dependent adenovirus diawali
dengan interaksi antara vektor Helper
Dependent Adenovirus dengan sel kanker, lalu dilanjutkan dengan ikatan
antara knob domain dari fiber protein dengan reseptor pada sel, yaitu CD46 dan
CAR. Mekanisme ini dilanjutkan dengan interaksi sekunder dimana motif pada basa
penton protein berinteraksi dengan molekul integrin. Ikatan dengan αv integrin akan
menstimulasi signaling sel dan menginduksi polimerisasi aktin untuk
memfasilitasi proses endositosis partikel virus (gen p53) melalui clathrin-coated pits (Morrisey et al., 2001).
Setelah vektor berhasil masuk
kedalam sel, endosome mengalami acidifikasi yang megakibatkan kapsid
terdisasosiasi dan gen p53 vektor masuk
kedalam sitoplasma. Proses dilanjutkan dengan replikasi DNA virus di
dalam inti dengan cara mensintesis protein virus di dalam sitoplasma. Kemudian
polipeptida hasil sintesis dirakit menjadi kapsomer di dalam sitoplasma. Di
dalam nukleus kapsomer dirakit menjadi kapsid dan kemudian DNA gen p53 masuk ke
dalam kapsid sel kanker (Baek et al., 2004). Dengan bantuan
mikrotubulus gen p53 mampu masuk kedalam nucleus melalui nuclear pore,
dilanjutkan dengan asosiasi dengan molekul histon. gen p53 akan menggantikan
posisi dari gen p53 yang mengalami LOH, mutasi maupun delesi, sehingga dengan
demikian fungsi p53 akan kembali normal.
Insersi gen p53oleh vektor helper dependent adenovirus dalam sel
kanker memicu sel untuk mengekspresikan p53
yang pada akhirnya mengaktifkan p21. P21 akan menghambat cyclin dan CDK
(cyclin D kinase) sehingga Rb tidak mengalami hiperfosforilasi dan E2F
tidak mampu mentranskripsi gen, sehingga sel akan mengalami “arrest”
pada perbatasan G1/S sebelum memasuki fase S. Dengan demikian, maka
progresivitas replikasi sel kanker dapat dihambat.
Mekanisme
Viroterapi Gen P53 Berbasis Helper
Dependent Adenovirus dalam Mediasi Apoptosis Sel Kanker
Pada penelitian Agarwal et al,. (1998) telah diketahui bahwa p53
mampu menghentikan pertumbuhan sel pada
G1 atau apoptosis. Pemberian vector adenovirus dengan gen p53 (Ad5CMVp53) meningkatkan
rasio G1/S pada siklus sel sekaligus meninhibisi pertumbuhan sel kanker
kolorektal melalui proses apoptosis (Baek et
al,. 2004). Insersi gen p53oleh
vektor helper dependent adenovirus dalam sel kanker memicu sel
untuk mengekspresikan peningkatan p53.
P53 berperan untuk mengaktifkan apoptosis melalui aktivasi transkripsi BAX.
Ketika BAX diaktifkan mitokondria akan melepaskan sitokrom c, akan terbentuk
kompleks BAX dengan APAF-1 (apoptosis-inducing factor 1),
procaspase 9 dan ATP. Dalam kompleks ini, procasapase 9 aktif sehingga menjadi
caspase 9 yang mampu mentrigger aktivasi caspase 3. Aktivasi caspase 3 akan
mengeksekusi sel dengan memecah DNA dan substrat lain sehingga menghasilkan
apoptosis sel kanker (Cotran et al., 2007).
Penelitian Eichhorst dan Krammer
(2001) menunjukkan bahwa level CD95 diregulasi oleh p53. Ketika kehilangan gen
p53 maka CD 95 juga akan menurun. Dengan adanya gen p53 yang diinsersikan oleh vektor
helper dependent adenovirus, maka akan terjadi peningkatan CD95 pada sel
kanker payudara. Peningkatan CD95 akan meningkatkan ikatan dengan ligannya
yaitu CD95L/Fas, CD95 mengalami trimerisasi dan sitoplasmiknya yang berupa death domain menarik protein FADD.
Protein FADD merekrut procaspase-8 yang nantinya akan teraktivasi melalui
pemecahan menjadi unit-unit yang lebih kecil berupa caspase 8. Caspase 8 akan mengaktivasi
caspase 3 yang akan mengeksekusi sel dengan memecah DNA dan substrat lain
sehingga menghasilkan apoptosis sel kanker (Cotran et
al., 2007). Dengan
demikian, dapat disimpulkan bahwa gen p53 yang diinsersikan melalui vektor helper
dependent adenovirus mampu
meregresi sel kanker melalui dual
mechanism dalam proses apoptosis, yaitu pelepasan sitokrom c oleh
mitokondria maupun death-induced
signaling complex.
DAFTAR PUSTAKA
Agarwal ML, Taylor WR, Chernov MV, Chernova OB, Stark GR.The p53
network. 1998 J Biol Chem; 273:
1-4.
Baek, Jeong-Heum ,Munna L Agarwal, Raymond R
Tubbs, Alex Vladisavljevic,Hiroshi Tomita, Ronald M Bukowski,Jeffrey W. Milsom,
Jin-Man Kim, Jin-Young Kwak. 2004. In vivo Recombinant Adenovirus mediated p53
Gene Therapy in aSyngeneic Rat Model for Colorectal Cancer. J Korean Med Sci; 19: 834-41
Cotran, Ramzi S dan Stanley
L. Robbins . 2007. Basic
Pathology. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.
Departemen Kesehatan Republik Indonesia
(Depkes RI). 2007. Aktivitas Fisik dan
Diet Seimbang Mencegah Kanker. http://www.promosikesehatan.com
/?act=news&id=473/.htm. Diakses tanggal 24 Agutus 2010. Pukul 16.40.
Eichhorst dan Krammer PH. , 2001. Derangement of apoptosis in cancer. Lancet 358:345
Finlay, Hinds, p.w. dan Levine. 1983. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation, Cell, 57:1083-1093.
Jusuf, Ahmad Aulia. 2009. Terapi Gen Pada Manusia. Bagian Histologi:Fakultas Kedokteran
Universitas Indonesia
Kartika. 2007. 800.000 Orang Indonesia Terserang Kanker
Tiap Tahun. http://www.suarapembaruan.com/News/2007/05/14/Utama/ut01.htm. diakses tanggal 21 Agustus 2010 pukul 15.10
Morrissey ,
Richard E., Christopher Horvath, Eileen A. Snyder, James Patrick dan James S.,
MacDonald. 2001. Rodent Nonclinical Safety Evaluation Studies of SCH 58500, an
Adenoviral Vector for the p53 Gene. Toxicological Sciences 65, 266-275
Sandig,
Volker, Rima Youil, Andrew J. Bett, Laura L. Franlin, Masanobu Oshima, Domenico
Maione, Fubao Wang, Michael L. Metzker, Rocco Savino dan C. Thomas Caskey.
2000. Optimization of the
helper-dependent adenovirus system for production and potency invivo .PNAS
vol. 97 no. 3 1002-1007
Sofyan, Rochestry. 2000. Terapi Kanker pada Tingkat Molekuler.Cermin Dunia Kedokteran No. 127
Survey
Kesehatan Rumah Tangga. 2001. Gizi dan Promosi Kesehatan. http://www.promosikesehatan.com/?act=article&id=122. Diakses tanggal 24 Agustus 2010. Pukul 16.54.
![]()